What is the Vagus Nerve (CN X)?
What is the Vagus nerve (CN X)?
The vagus nerve controls many crucial bodily functions, including mood, immune response, digestion, and heart rate. It establishes one of the connections between the brain and the gastrointestinal tract and sends information about the state of the internal organs to the brain. Colic could be associated with subluxations or spinal nerve interference, particularly in the region of the vagus nerves, which could explain the relationship between colic, stomach and digestive issues.
It seems to be very clear how realigning the atlas can affect the activity of the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve is the tenth of twelve cranial nerves that originate in the brain stem and regulate the unconscious operation of organs. These nerves communicate via pathways that can impact respiration, digestion, and heart rate. These pathways make sure to signal non-emergency states in the body and shift into states of rest and healing. If it runs opposite signals to activate fight-or-flight responses, the continuous high-stress levels make the body vulnerable to damage.
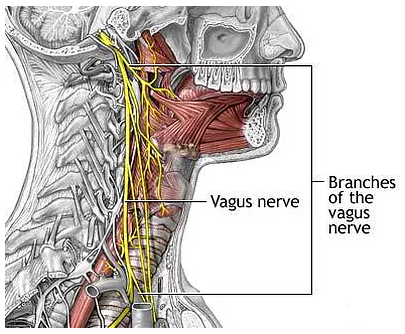
Infantile Colic and Vagus Nerve
“100 newborns were physically examined and assessed for structural dysfunctions of the spinal column. 99% of these newborns had at least one immovable joint between bones in the upper cervical and occiput region.”
What is Infantile colic? Infantile colic is a common condition affecting approximately one out of every four infants. The condition is characterized by inconsolable crying and stomach sensitivity in seemingly normal babies. The cause of colic is still unknown although research has shown that subtle spinal nerve interference, often due to the rigors and stress of routine birthing procedures can be a contributing factor.
“Relationship between the activity of the vagus nerve and pathophysiology linked to diseases.”
Dr. De Couck M., Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy in Belgium, published an article about the link between the vagus nerve and pathophysiology. The article provides evidence for the hypothesis that adequate vagal nerve activity reduces the risk of major diseases, via common basic mechanisms and interim risk factors. These diseases include cardiovascular disease, cancer,Alzheimer’s disease and the metabolic syndrome. Three basic mechanisms contribute to such illnesses: local oxidative stress and DNA damage, inflammatory reactions and excessive sympathetic responses, all of which are inhibited by vagal nerve activity.
Reference
– Image Source, Vagus Nerve Stimulation & Repair, Medium, Link
– Image Source 2, Yoga is about the breathing!, Yoganatomy, Link
– The Vagus Nerve – A Pathway to Health, Link
– Waddington, E. Incidence of somatic dysfunction in newborns. J. Am Osteo. Assoc 2015 Nov; 115(11): 654-65